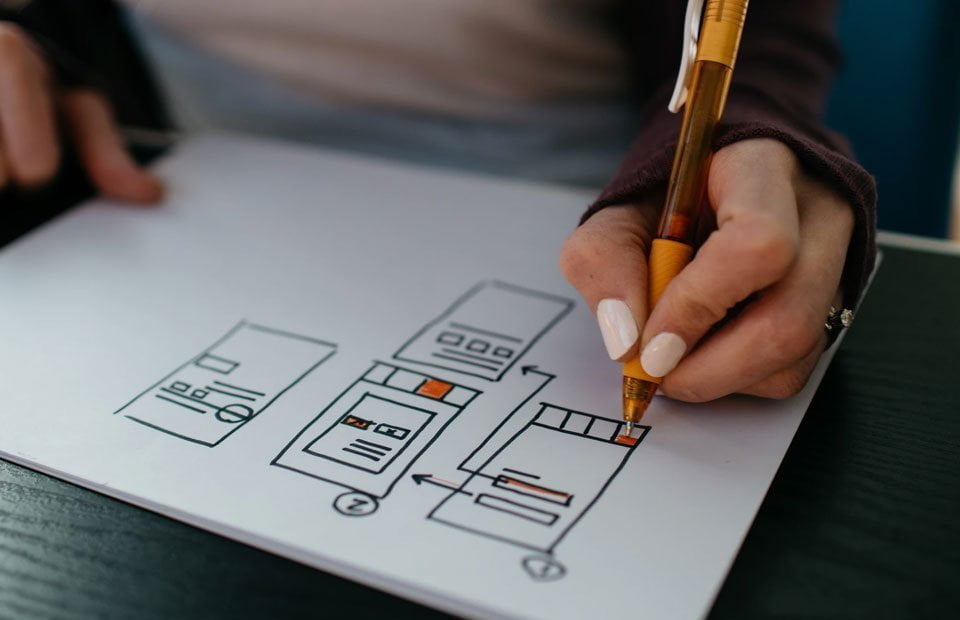
What is UX Design?
UX design refers to the overall experience a person has of using a product or service, particularly in terms of how easy, enjoyable, and useful it is. It includes all interactions a person has with a system, including its look, feel, usability, and the emotions and attitudes resulting from these interactions.

In the context of design and technology, UX is commonly used to refer to the creation and structure of websites, software, and other digital solutions. It is a multidisciplinary field that combines elements of visual aesthetics, user psychology, and technology to develop systems that are easy to use, visually appealing, and effective in meeting user needs.
Good user experience is important because it can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty, and it can also have a positive impact on a company’s bottom line. Companies that prioritize UX in their design and development process often see increases in sales, customer retention, and brand reputation.
- Usable: The products should offer simplicity, ease of use, and familiarity to users.
- Useful: A product must fill a need. If the product isn’t filling a perceived gap in the users’ lives, then there is no real reason for them to use it.
- Desirable: The product’s visual aesthetics should be appealing and evoke positive emotions.
- Findable: Users should easily find solutions to problems encountered with the products.
- Accessible: The product or service must be usable by everyone, including those with disabilities.
- Credible: The company and its offerings must inspire trust and reliability.
Similarly, in digital creation, UX means everything that affects a user’s interaction with a digital solution. When people use a product, they typically evaluate their experiences based on the following criteria:
Value: Does this product give me value?
Function: Does this product work?
Usability: Is it easy to use?
General impression: Is it pleasant to use?
Terms of UX Design
Many terms are used in the field of UX. Some of the most common of these are:
-
User-centered design: This approach focuses on the needs, desires, and limitations of the user rather than the desires of the designer or business.
-
Usability: The ease with which a solution can be used to achieve a desired goal.
-
User interface (UI): The visual creation and layout arrangement of a system, including the buttons, menus, and other elements that users interact with.
-
User-journey: The series of steps users follow when using a product or service, including the actions they take and the emotions they experience.
-
User-flow: A diagram that shows the steps a user goes through while using a system, and the various paths they can take.
-
Wireframing: The process of creating a rough design of a website or app, including the placement of elements like buttons, menus, and text.
-
Prototyping: Creating a rough version of a system that is used to test and refine ideas before creating a final version.
-
A/B testing: A method of comparing two versions of a system to choose which version performs better, where users are randomly given one of the two versions and their behavior is measured.
-
User-research: The collection of data about users and their needs, wants, and behaviors, through methods such as interviews, surveys, and usability testing.
-
User-personas: A fictional representation of a typical user, based on their research data.
Also Read: User Interface (UI) design and what are Fundamentals
Process of UX Design
The UX design process involves various steps, and the specific steps may vary depending on the specific products or services being designed and the goals of the creative team.
In general, however, the process of UX design includes the following steps:
- Research and planning: This stage involves gathering information about the target users, their needs and goals, and the market and competition. This can include user-research methods such as interviews, surveys, and usability testing.
- Ideation and concept development: In this stage, the team generates ideas and develops a concept for how it will work. This might include building user-personas, sketching wireframes, or creating prototypes.
- Design and prototyping: In this stage, the team makes a more detailed and advanced version. This can include creating high-fidelity wireframes, creating visual designs, and building functional prototypes.
- Testing and evaluation: In this stage, the team tests the products or services with real users to gather feedback and make improvements. This might involve usability testing, A/B testing, and other methods.
- Launch and ongoing improvement: After the solution has been launched, the team may continue to gather feedback and make improvements to enhance the user experience over time.
It’s important to note that UX design is an iterative process, and it’s common for the team to go back and forth between different stages as they gather feedback, test ideas, and make improvements.
Check out our article on Figma for more about UX Design Systems! https://help.figma.com/hc/en-us/sections/14548397990423-Course-Introduction-to-design-systems